Virtual Reality (VR): Definition, Factors & Function
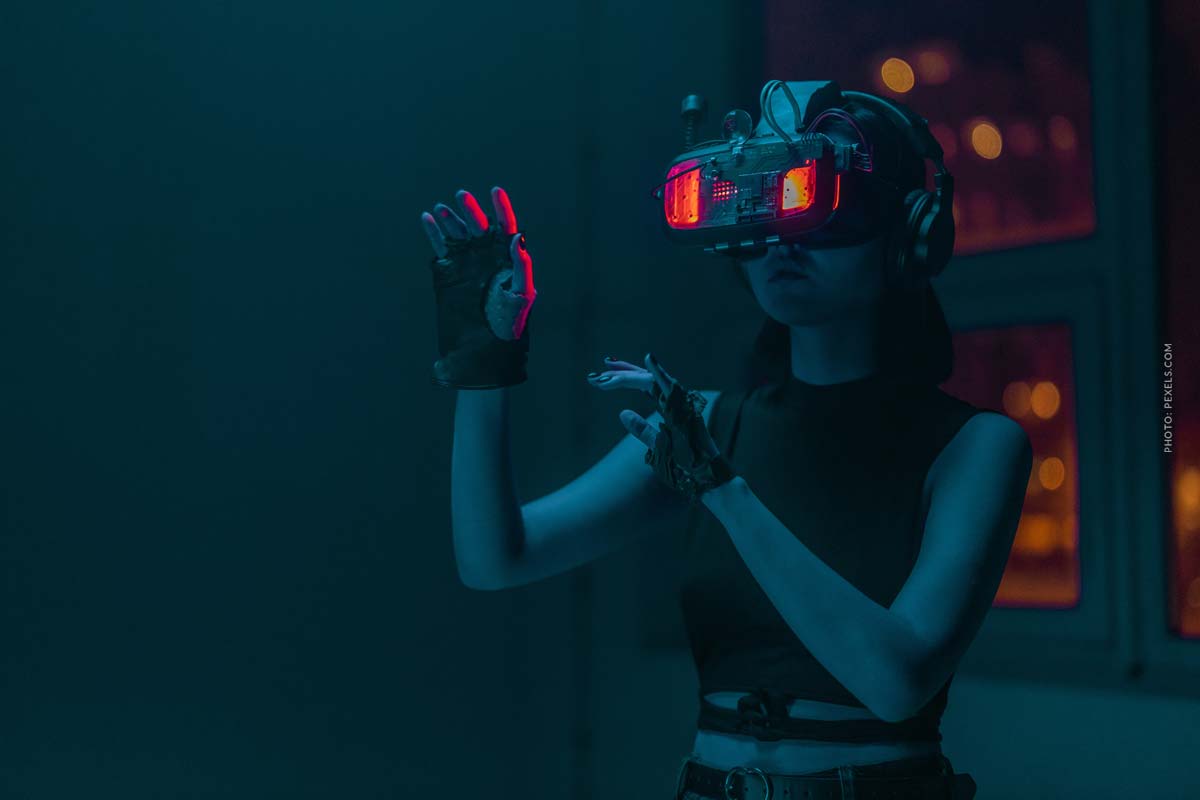
Virtual reality, or VR for short, translates as virtual reality and means the perception of a virtual world that is not real, but whose effect or functionality is present and can be experienced accordingly.
What factors define VR?
VR is defined by a few factors. Theoretically, there are no limits. Nevertheless, these are the basic factors:
- 360 degree environment
- 3D depth effect
- Spatial audio
- Motion control
According to VR researcher Jeremy Bailenson, the use of VR is particularly valuable when real-world experiences are dangerous, impossible, expensive, or rare. Accordingly, it is particularly well suited for
- Expensive experiences with only a small audience
- Dangerous, high-risk experiences, such as high-risk climbing trips
- Extraordinary experiences, like flying like a bird
- Experiences rarely experienced in reality, such as the surfacing of a whale
How does VR work?
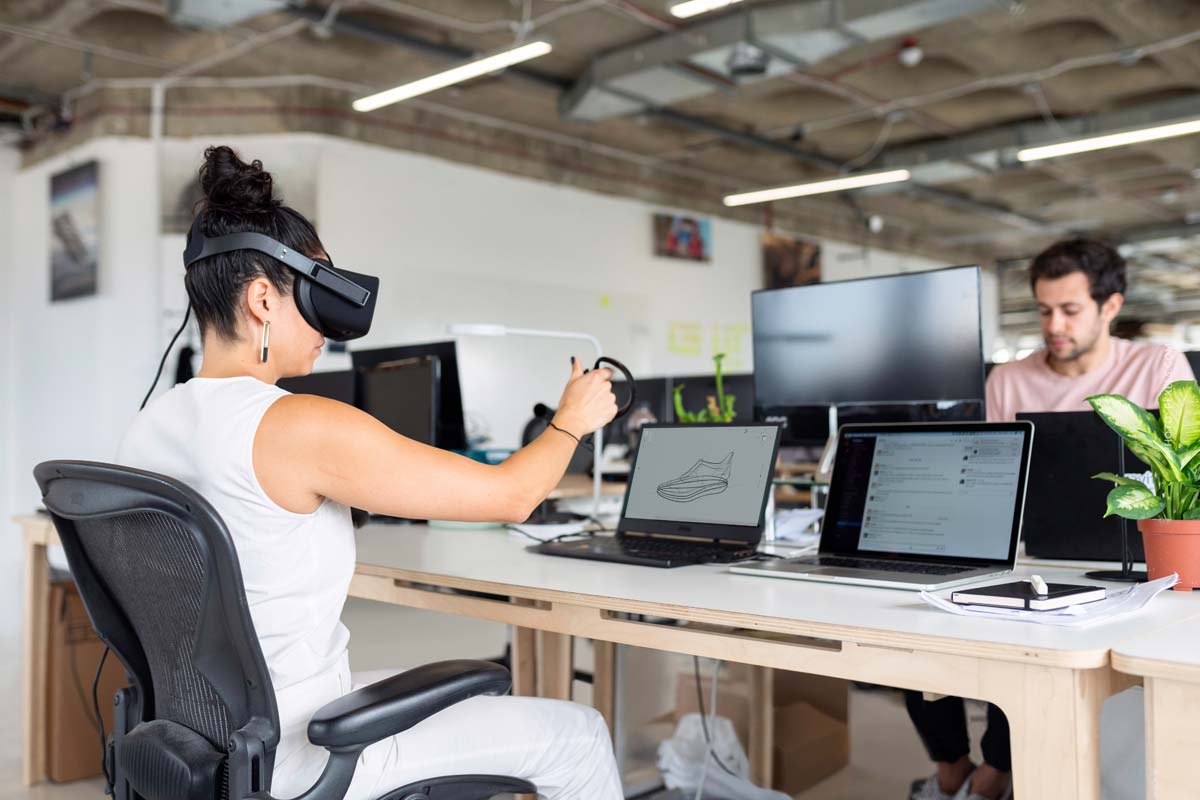
We can only experience experiences on a screen from a certain distance. In VR, you are in the middle of the action because things are happening around you. Depending on the application, you only need one pair of VR glasses. VR goggles consist of two lenses that create a separate image for each eye. There are also VR controllers that are handy for interaction. Otherwise, you only need free space to move around freely so that you can absorb the experiences in the best possible way.